Advantages and Disadvantages of a Subscription Business
Wonder if the subscription business model is worth it?
Learn about the pros and cons of subscription businesses in this article.
Nowadays, subscription-based businesses are rather common, and one of the main reasons for the popularity of this business model is the fact that subscription businesses grow revenues 5-8 times faster than traditional models. An average person has at least one, if not several, subscriptions for certain services. Subscription business is thriving indeed, in 2024 alone, 96% of subscription professionals expected their revenue to increase, which was a rather confident prognosis. Indeed, such a popular business model seems like a great option for a business. However, is it a perfect choice? In this article, we explore the common types of subscription businesses and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the subscription business model. Additionally, we give practical advice on how to deal with certain subscription business problems, ensuring uninterrupted growth of your establishment.

What Is a Subscription Business?
So, what is a subscription business model? Instead of a single purchase, this model involves customers paying a regular fee for ongoing access to a product or service, typically billed monthly or annually, with frequency options available. This structure fosters a predictable revenue stream for businesses, allowing for better financial planning and investment. Furthermore, it encourages long-term customer relationships, as businesses focus on providing consistent value and service to retain subscribers. Subscription businesses come in various types and shapes, so let’s talk about subscription business types below.
Types of Subscription Businesses
While subscription businesses have a common primary feature, not all of them are the same. Such companies offer different services, which means adopting a subscription business model is convenient for establishments from various spheres. The subscription business model often manifests in one of the following types.
Product Subscription
Businesses of this type offer their customers a shipment of physical products. The variety is endless: flowers, garden appliances, cosmetic products, accessories, foods, pet treats — anything can be delivered regularly (daily, weekly, monthly) if a client subscribes. A great example of such a business is Blue Apron, which offers a subscription service that provides customers with pre-portioned ingredients and heat-and-eat meals.
Content Subscription
This type of subscription service provides customers with access to digital or physical content sources. This includes books, magazines, videos, music, etc. For example, Bookroo sends curated children's books each month, directly to the homes of parents and grandparents. Other popular examples of such a business are Netflix and HBO Max — streaming services that grant clients access to movies and TV series. Such companies can also provide a free version of the application with ads and a premium ad-free version for a subscription fee.
Software Subscription
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) is one of the most common examples of a subscription business. This model provides access to software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for customers to purchase and install software locally. To continue using the software, clients must pay subscription fees regularly. For instance, Microsoft 365 gives customers access to Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and other programs for a yearly or a monthly payment.
Membership
This subscription model slightly differs from the rest. While previous types of subscription businesses provided clients with products, a membership gives customers access to privileges. A typical example of such a business type is supermarket chains' memberships, such as Target Circle. For a fixed monthly or yearly subscription fee, clients can receive membership discounts, extra days on top of the regular return window, free deliveries, and other perks. Such a model creates a sense of community among customers, fostering loyalty to the establishment.
Pros of the Subscription Business Model
Nowadays, more and more companies are adopting the subscription business model. And there are good reasons for that. Below, we list the benefits of a subscription business model you should consider.
Consistent Revenue Flow
When it comes to one-time purchases, it might be challenging to determine when the customer makes the next one. The ability to predict monthly income is a significant advantage of subscription models. Unlike websites with variable product popularity, subscriptions provide a consistent revenue stream through fixed pricing and guaranteed deliveries. This stability is extremely convenient for merchants in every field. Furthermore, this financial security improves the establishment’s budgeting, creating opportunities for investment in innovation and building resilience against economic challenges.
Better Customer-Company Bonds
One-time sales businesses rarely get the opportunity to engage with clients for an extended period of time, which minimizes the chance of repeat purchases. Subscription models, however, provide sellers a continuous opportunity to engage with customers and build relationships. This extended interaction fosters trust among customers, enhancing loyalty to the brand. Customer loyalty transforms purchases into habits, leading to increased referrals, boosting sales and growth of the company.
Enhanced Product Management
A major challenge for e-commerce stores is managing inventory costs due to uncertain demand. As subscription models provide predictable monthly sales figures, merchants get a chance to improve their inventory management and enhance demand forecasting. This helps sellers save money on supplies and rent for storage units, as with a more precise demand prediction, there's decreased risk of overspending on manufacturing and keeping products that won't translate into revenue.
Upselling Opportunities
Another benefit of subscription businesses is that such models offer excellent opportunities for upselling and cross-selling. Companies can present higher-level subscription plans with advanced features, pushing users to upgrade. Furthermore, such businesses can promote complementary products or services to subscribers, increasing per-customer revenue. Such strategies help merchants avoid losing sales opportunities and improve overall income, boosting the company's growth.

Cons of the Subscription Business Model
While the subscription business model offers many benefits, it also comes with several disadvantages. Here, we explore the common subscription business issues you must pay attention to when choosing a model for your establishment.
High Competition
The subscription market is intensely competitive and demands constant improvement to prevent rivals from surpassing your offerings. To stay in this field, it is vital to provide your clients with benefits for staying loyal to your establishment and unique offers. Customer perks like discounts or complimentary delivery can significantly minimize churn and boost retention. Being creative in giving potential and regular clients reasons to choose your brand over your competitors is crucial to survive in this industry, and that requires enormous effort.
Client Acquisition
Purchasing a product one time is simple and convenient; subscribing, however, requires regular expenses, and not all people are ready to commit to that. Thus, gaining subscribers can be extremely difficult for businesses. Attracting new subscribers demands substantial investment, as effective marketing and promotional campaigns are crucial for conversion. The company’s task is to convince potential clients of the value of their product, which might require a lot of work.
Retention Complications
Recent reports show that, on average, only 30% of subscription business clients are loyal customers, yet they bring 80% of the overall revenue, which makes it essential to work on retention rate. High churn rates can pose a significant threat to the stability of subscription-based businesses. While subscriptions offer consistent income, it is important to consider potential issues carefully. Maintaining customer satisfaction and preventing subscription cancellations requires a proactive, creative approach. It is essential to build transparent customer relations, especially regarding cancellation policies and possible extra fees. Minimizing churn through preventive strategic planning and customer-oriented tactics is necessary for long-term success.
Subscription Management
Efficient contract management is crucial for businesses of all sizes, especially when dealing with subscriptions. These contracts include critical information, such as payment methods, card details, and delivery schedules. All these elements are vital for timely shipping or service providing. Manually navigating these complexities can be highly tedious, leading to potential errors and delays, increasing the risk of customer dissatisfaction. Fortunately, you can manage subscriptions more efficiently with the Germius subscription manager.
Tactics to Resolve Common Subscription Business Issues
Issues exist within any business; fortunately, often there are solutions that can resolve them or minimize their impact. Here, we advise on how to deal with common subscription business model problems, ensuring the stable development of your company and consistent revenue.
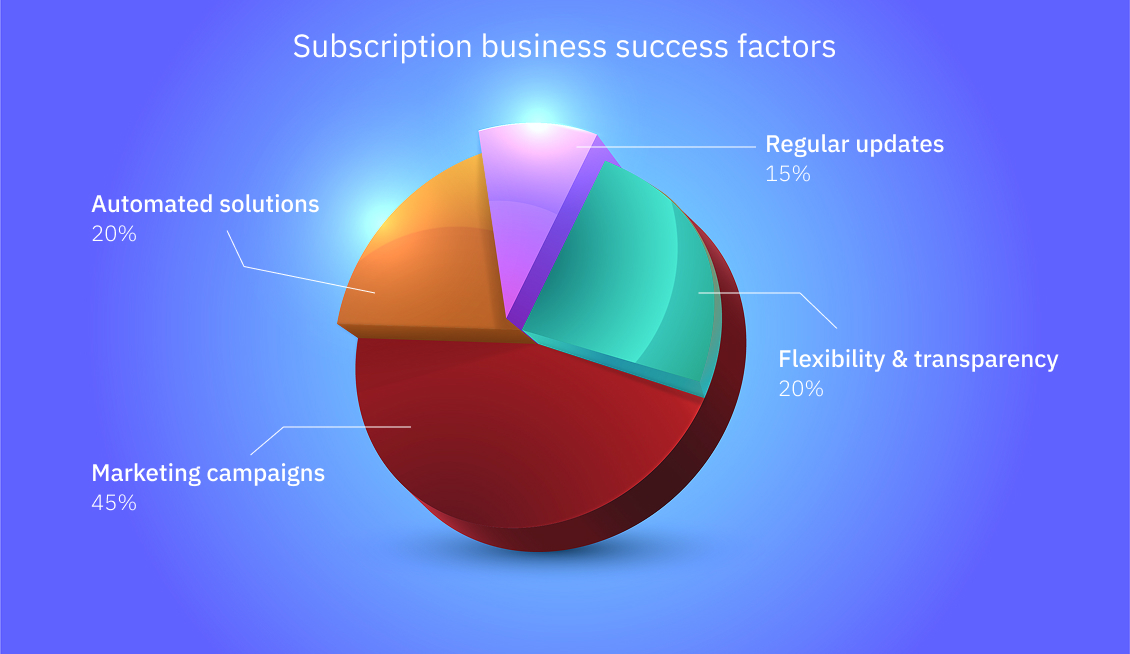
-
Flexibility and transparency.
To reduce customer hesitation in commitment to the brand, companies must offer flexible subscription options, transparent pricing, and clear cancellation policies. Highlighting cost savings and exclusive access of subscription plans is crucial to address potential concerns effectively. -
Marketing campaigns.
Efficient advertisement strategies are vital for attracting potential customers and keeping the regulars. Investing in CRM software, such as Germius CRM, to manage customer-company relationships and collect valuable client information might be a great option to enhance your advertisement. -
Regular updates.
While sellers might be satisfied with current revenue, in a competitive subscription business sphere, constantly improving is crucial. Create new products, make seasonal or holiday-related offers, and adjust the current services to the demands of clients to stay relevant in the subscription field. -
Automated solutions.
Instead of managing subscription information manually, sellers can invest in subscription manager programs, such as one available within Germius. This will allow for efficient data and revenue management, while saving time.
Analyze your sales data and customer feedback regularly to identify weaknesses in your performance and make the necessary improvements. The proactive adjustments will prevent minor issues from escalating into significant problems. Furthermore, by paying attention to key metrics, you will get a chance to recognize starting trends and take the opportunity to enhance your revenue, ensuring the adaptability of your business to market changes.
Conclusion
The subscription business model is extremely popular today, and there are several reasons for that: constant revenue flow and predictable income, increased customer retention, and upselling and cross-selling opportunities push many businesses to adopt it. However, before choosing this model, sellers must also consider its downsides, such as high competition in the field, customer acquisition and retention complications, and subscription management issues. Fortunately, subscription businesses can overcome such challenges by fostering trust between clients and the company, investing in advertising and automated solutions, and updating products. We hope our article was helpful and that its information will help you make decisions to enhance your business’s growth.


